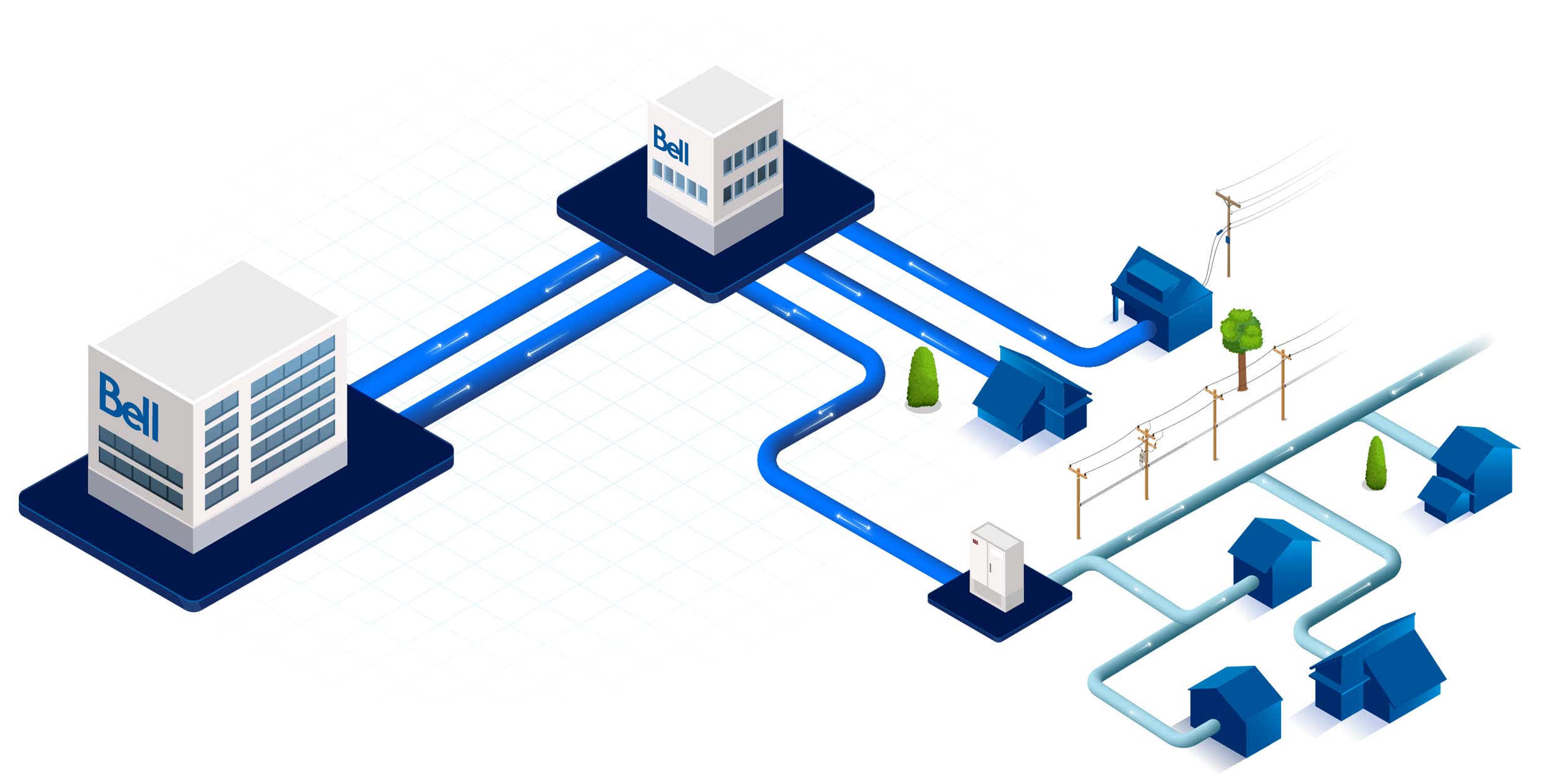
How our award-winning networks work
Both of our networks are built with fibres, bringing the best experiences to our customers.
Fibre-optic cables are made of hundreds of thin strands of glass – or fibres – each about one-tenth the size of a human hair. These cables are installed in a sophisticated network of paths that can be overhead, underground or underwater, depending on location.
Unlike traditional copper cables, fibre cables use light instead of electricity to transmit data, making them faster and more reliable. With a fibre connection your data literally moves at the speed of light and you get consistently fast upload and download speeds.
-
Data centres
-
Central offices
-
Fibre distribution
-
Fibre-to-the-home
-
Fibre-to-the-
neighbourhood
Our journey from
copper to fibre
For years, copper wires were the backbone of our networks. With the introduction of fibre technology, Bell took a leadership role in building out fibre networks to bring Canadians the fastest and most reliable network technology. Our initiative to replace copper cables with fibre ones requires an investment of billions of dollars, but the paybacks are substantial – customers will enjoy better connectivity and the environment will be better for it.
| Fibre | Copper | |
|---|---|---|
| Faster data transmission |
Data is translated into light pulses, then sent along a fibre within the cable. Once they reach their destination, the light pulses are converted into webpages, emails, television show streams, video calls, and more. | Data is translated into electric pulses, then travels along the copper cables. Once they arrive at the receiving end, the electric pulses are converted back into the original data form. |
| Faster speeds | Customers can get the fastest speeds with Bell pure fibre Internet. Future fibre upgrades will deliver even faster speeds to more Canadians. | Customers can get speeds of up to 100 Mbps with copper-based Internet services. |
| Reliable technology |
Fibre cables aren’t affected by electromagnetic interference because they use light to transmit data, not electricity. Fibre is also more durable and less impacted by environmental issues, such as water or extreme temperatures. | Because they are electrical conductors, copper cables can be affected by electrical interference and environmental factors, causing deterioration over time. |
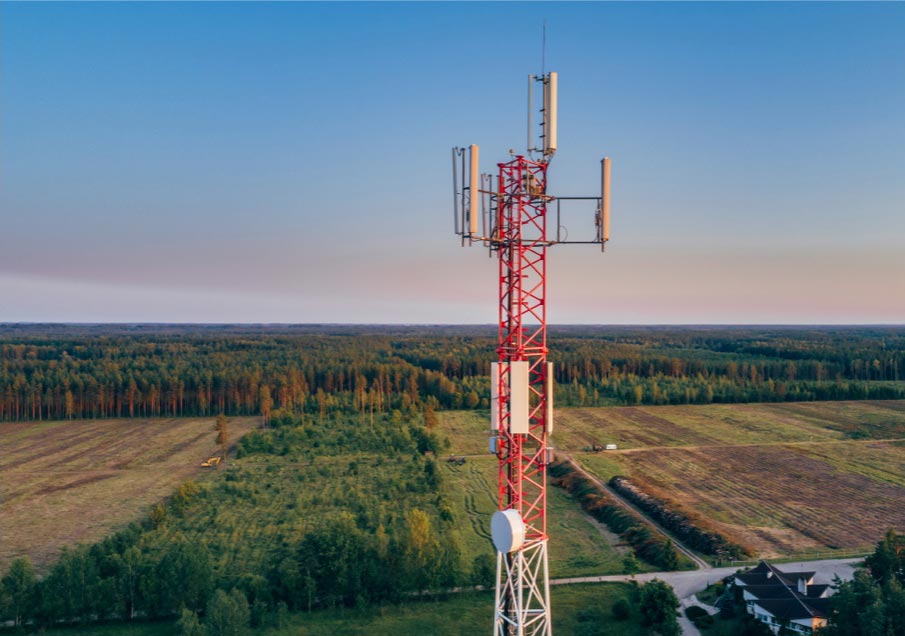
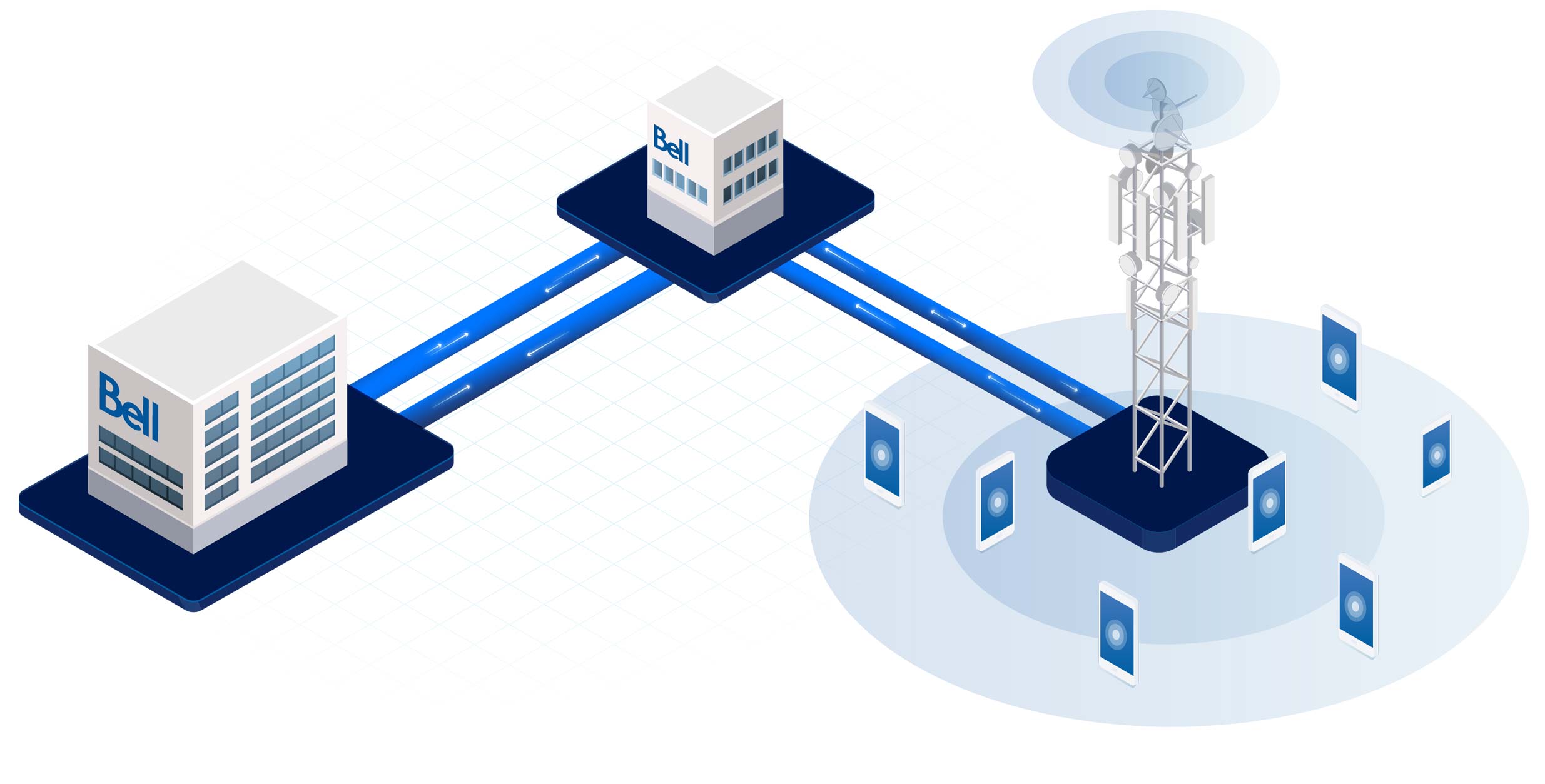
Cellular networks are made up of cells (also known as cell sites), which provide wireless connectivity to a geographical area. The size of these cell sites varies and is based on location, terrain, and population density. For example, in urban areas with higher population density and more network usage, there tend to be more cell sites that are smaller in size.
The Bell network is made up of over 25,000 cell sites across the country, covering 99% of the Canadian population1. Cell sites are connected to our extensive fibre-optic network, the world’s best network technology, for a faster and more reliable connection.
-
Data centres
-
Central offices
-
Cell sites
-
Mobile devices



















